Hand Router
Make: Porter Cable
Model: 8902
Ace: Needed (Makerhub@georgefox.edu).
Location: Wood Shop
Description
The hand router is very versatile but can also be a very dangerous tool if not used properly. Used in conjunction with the proper jigs and templates, the router can accomplish a wide variety of tasks with relative ease. Holes and channels of varying depths and nearly limitless shapes can be cut. The router can also use special bits to cut bevels and chamfers along the edges of a workpiece.
Introductory Video]
Introductory Video]
About Direction of Cut]
Documentation
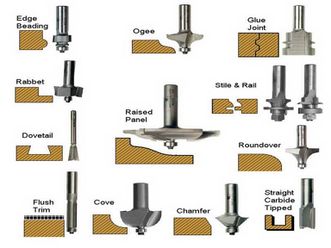
Terminology
Each bit is made for a different job. The wood shop has a wide assortment, although less common types may be unavailable. It should be noted that different bit sizes and profiles will operate better at different speeds. The amount of material the is being removed in each pass as well as the hardness of the wood should determine the speed the router is ran at. With reference to straight bits, if the bit is less than 1" in diameter, many recommend speeds near 24,000 rpm. For bits 1" - 2.5", 16,000 to 18,000 rpm, 2.5" to 3", 12,000 to 14,000 rpm, and for bits of more than 3", a common recommendation is 10,000 to 12,000 rpm.
Occasionally routing can leave burn marks on the workpiece. This usually means that the bit in the router has become dull, let a shop supervisor know if a bit seems dull. Sometimes the burning is due to build up of resin and other gunk (a technical term) on the back of the blade insulating the bit and allowing for heat to build up, make sure to keep bits clean. A final possible cause of burning wood while routing is taking passes that are too slow or setting the router bit speed too high.
Training
Overview
Insert Text
Demonstration
Demonstrate you can safely setup the hand router tooling and edge a piece of material. Remember to always unplug the router when changing tools or making adjustments to prevent an accidental turn on situation. The direction of travel is also important when making cuts to prevent tearing out corners and edges. Use router bits with bearings to help guide the cutter. Never attempt to free hand a cut without a guide for the router to follow as this can lead to the router running away out of control.
General Procedure
Insert text
Safety
Certification
Troubleshooting
If you notice burning on the material it could be caused by feeding the cutter at too slow of a rate. A dull cutter can also cause material burning.
Maintenance
General maintenance
- Make sure cutter bits are clean.
- Remove and clean the collets as needed.
- Make sure any adjustment screws are tight.
Specific Maintenance Tasks
| Maintenance Procedure | Frequency | Done By |
|---|---|---|
| Sample | Sample | Sample |