Difference between revisions of "Virtual Reality Welding Station"
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
* Weld Metal/Electrode - The metal added to the base metal to create a weld. | * Weld Metal/Electrode - The metal added to the base metal to create a weld. | ||
* Torch - The piece that is held while welding and feeds the weld metal into the base metal. | * Torch - The piece that is held while welding and feeds the weld metal into the base metal. | ||
| − | * MIG - Metal inert gas is a welding process in which an electric arc forms between a consumable MIG wire electrode and the base metal, which heats the base metal, causing them to melt and join. Along with the wire electrode, a shielding gas feeds through the welding torch, which shields the process from contaminants in the air. This is the easiest and most common type of welding and it is recommended that you start with this method. | + | * MIG Welding - Metal inert gas is a welding process in which an electric arc forms between a consumable MIG wire electrode and the base metal, which heats the base metal, causing them to melt and join. Along with the wire electrode, a shielding gas feeds through the welding torch, which shields the process from contaminants in the air. This is the easiest and most common type of welding and it is recommended that you start with this method. |
| − | * TIG - Tungsten inert gas is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area and electrode is protected from oxidation or other atmospheric contamination by an inert shielding gas (argon or helium), and a filler metal is normally used, though some welds, known as autogenous welds, do not require it. This is difficult to master but provides great control when creating a weld. It is also useful for welding many metals besides steel. | + | * TIG Welding - Tungsten inert gas is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area and electrode is protected from oxidation or other atmospheric contamination by an inert shielding gas (argon or helium), and a filler metal is normally used, though some welds, known as autogenous welds, do not require it. This is difficult to master but provides great control when creating a weld. It is also useful for welding many metals besides steel. |
| − | * Stick - A manual arc welding process that uses a consumable electrode covered with a flux to lay the weld. An electric current, in the form of either alternating current or direct current from a welding power supply, is used to form an electric arc between the electrode and the metals to be joined. The workpiece and the electrode melts forming a pool of molten metal (weld pool) that cools to form a joint. As the weld is laid, the flux coating of the electrode disintegrates, giving off vapors that serve as a shielding gas and providing a layer of slag, both of which protect the weld area from atmospheric contamination. This is the oldest form of welding and is still popular; however there is not a stick welder in the maker hub. | + | * Stick Welding - A manual arc welding process that uses a consumable electrode covered with a flux to lay the weld. An electric current, in the form of either alternating current or direct current from a welding power supply, is used to form an electric arc between the electrode and the metals to be joined. The workpiece and the electrode melts forming a pool of molten metal (weld pool) that cools to form a joint. As the weld is laid, the flux coating of the electrode disintegrates, giving off vapors that serve as a shielding gas and providing a layer of slag, both of which protect the weld area from atmospheric contamination. This is the oldest form of welding and is still popular; however there is not a stick welder in the maker hub. |
'''[https://www.millerwelds.com/files/owners-manuals/O276533H_MIL.pdf User Manual]''' | '''[https://www.millerwelds.com/files/owners-manuals/O276533H_MIL.pdf User Manual]''' | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
====Overview==== | ====Overview==== | ||
| − | + | The operation of the AR Welding station is simple. First you will select a torch for the type of weld you want to practice and plug in the machine. After that it is a simple matter of setting up an exercise based on difficulty, welding method, and weld type. It is recommended that you start with the pre-programmed exercise to begin and then move on to custom exercises as you become more experienced. The general weld type is determined by what piece is being welded; the options include liner and cylindrical butt, lap, and T joints. Before the exercise begins you will have to calibrate the AR helmet. The calibration process occurs at the beginning of the exercise and is completed by following the instructions given by the AR helmet. After the calibration is completed complete the exercise, view the results, and then repeat. | |
====Demonstration==== | ====Demonstration==== | ||
| − | + | With the virtual reality welder, students will get the idea as to how the welding machines work, whether that be arc, MIG, or TIG welding. Once students earn a score of 90 or higher on the simulation, they have the opportunity to work with the actual welders in the welding shop. | |
====General Procedure==== | ====General Procedure==== | ||
| − | + | Setting up Simulator | |
| + | # Plug in extension cord (make sure it won’t trip anyone) for power. | ||
| + | # Flip switch on back of machine to turn on. | ||
| + | # Press power button on the front of the machine and wait for the system to start up. | ||
| + | # Attach welding process of your choice (see welding processes section down below). | ||
| + | # At login screen, select user. Guest works well. | ||
| + | # Select right or left handed. This is important because it affects the angle the torch should be held at when performing an exercise. | ||
| + | # Open an exercise. There are four choices for creating an exercise: Open, GMAW (MIG), GTAW (TIG), SMAW (Stick). If you know what type of weld you want to practice go for the open exercise because it will allow for the most customization. If this is a new experience, select the type of weld you are practicing and roll with one of the preset courses. | ||
| + | # On the top of the screen the welding parameters are displayed and will be in red if they are not set properly. Use the control panel (pictured below) to adjust them as needed.[[File:Weld Panel.png|none|thumb|594x594px| (1) Power On/Off Button Use button to turn system on and off. (2) Helmet Light Control Use button to turn helmet light on and off, and change intensity of light. (3) Filler Rod Light Control (TIG) Control not used with latest software. (4) Volume Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease volume of helmet speakers. (5) Display (Zoom) Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to magnify images on display screens. (6) Augmented Reality (AR) Button Use button to turn augmented reality feature on and off. (7) System Settings Button Use button to access system settings menu. Use the settings menu to change language, units of measure (standard or metric), camera settings and other parameters. After starting an exercise, use the System Settings button to adjust video device settings and optimize AR tracking for the room lighting conditions. (8) Clean Slag Button Use button to remove slag from augmented reality workpiece when Stick and FCAW welding. Slag must be cleaned for test results to be displayed. (9) Shielding Gas Flow Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease the shielding gas flow for the MIG and TIG weld processes. (10) Gun Trigger Selection Button Use button to select either two-step or four-step trigger operation. (11) Amperage/Wire Feed Speed Selection Button Use button to select the weld parameter (amperage or wire feed speed) to be adjusted (see Item 12). (12) Amperage/Wire Feed Speed Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease amperage or wire feed speed (see item 11). (13) AC/Polarity Selection Button Use button to select AC weld output or DCEP or DCEN weld polarity. (14) Voltage Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease weld voltage. (15) System Navigation Buttons Use buttons to navigate AR system programs and select menu items. (16) OK (System Selection) Button Use button to activate selected menu items. (17) System Cancel Button Use button to stop the AR program or activity in use, or return to the previous screen. ]] | ||
| + | # Place Helmet on head and size to head. | ||
| + | # Follow instructions in the helmet to calibrate the simulator to begin welding. | ||
| + | # Press cancel to exit. There is also an option to view results that is very helpful. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Switching Welding Processes | ||
| + | |||
| + | MIG: | ||
| + | # Take connector of MIG torch and align 4 holes with machine (left side). | ||
| + | # Twist the threaded end, but do not over tighten. | ||
| + | # To remove, unscrew the connector. | ||
| + | Stick | ||
| + | # Grab clamp with small cord attached. | ||
| + | # Align pins with the 5 holes of the connector with the receptacle on the machine (right side). | ||
| + | # To remove, press silver button and softly pull straight out (do not twist). | ||
| + | TIG | ||
| + | # Grab cable with TIG torch attached. | ||
| + | # Align 4 holes of the connector with the receptacle on the machine (left side - same as MIG). | ||
| + | # Screw in while holding the connector (do not over tighten). | ||
| + | # To remove, unscrew the connector. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Clean up | ||
| + | # Take helmet off and place on 2nd shelf of cart. | ||
| + | # Disconnect welding process. | ||
| + | # Exit out of the exercise. | ||
| + | # Press power button on front of the machine and wait for screen to be completely blank. | ||
| + | # Flip the switch to off on the back of machine. | ||
| + | # Unplug the extension cord and leave it coiled up neatly underneath the cart. | ||
| + | # Stack work pieces neatly. | ||
| + | # Coil up all cables of torches used and neatly place on the bottom shelf of the cart. | ||
==Safety== | ==Safety== | ||
| − | + | * Don’t drop the helmet, always place on cart when your not wearing it | |
| − | + | * When someone enters the tool room, make sure they know about the extension cord | |
| + | * Do not aggressively over tighten the connectors of the welding torches | ||
| + | * Make sure to press silver button when releasing the connector of the stick torch | ||
| + | * Do not cut power to the machine before it is completely shut down (clean up #4 & #5) | ||
| + | * Always lay torches completely on top of the table | ||
| + | * Make sure overhead clamp is secured tightly before using | ||
| + | * Do not scratch the coupons as the simulator needs the markings to read your weld. | ||
| + | * | ||
==Certification== | ==Certification== | ||
| Line 68: | Line 112: | ||
==Maintenance== | ==Maintenance== | ||
====General maintenance==== | ====General maintenance==== | ||
| − | + | * Make sure the space is kept neat and tidy. | |
| − | + | * Dust off the top of the machine if necessary. | |
| + | * Before leaving, make sure all cords and torches are in their place. | ||
====Specific Maintenance Tasks==== | ====Specific Maintenance Tasks==== | ||
| Line 81: | Line 126: | ||
|Sample | |Sample | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 10:30, 12 June 2019
Make: Miller
Model: Augmented Arc Welding Simulator
Ace: Wyatt Bertis (wbertis22@georgefox.edu).
Location: The Vault
Description
The virtual reality welder is the industry’s most realistic welding simulation solution for classroom training. For beginner to advanced-level weld students, the AugmentedArc System simulates multiple welding processes, blending real-world and computer-generated images into a unique, augmented reality environment. Below is an example of this piece of equipment being used.
Documentation
Terminology
- Base metal - The metal pieces that are being joined together. For the simulator there are several base metal configurations in the form of the blue coupons.
- Coupons - Small pieces of metal used to practice welding.
- Weld Metal/Electrode - The metal added to the base metal to create a weld.
- Torch - The piece that is held while welding and feeds the weld metal into the base metal.
- MIG Welding - Metal inert gas is a welding process in which an electric arc forms between a consumable MIG wire electrode and the base metal, which heats the base metal, causing them to melt and join. Along with the wire electrode, a shielding gas feeds through the welding torch, which shields the process from contaminants in the air. This is the easiest and most common type of welding and it is recommended that you start with this method.
- TIG Welding - Tungsten inert gas is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area and electrode is protected from oxidation or other atmospheric contamination by an inert shielding gas (argon or helium), and a filler metal is normally used, though some welds, known as autogenous welds, do not require it. This is difficult to master but provides great control when creating a weld. It is also useful for welding many metals besides steel.
- Stick Welding - A manual arc welding process that uses a consumable electrode covered with a flux to lay the weld. An electric current, in the form of either alternating current or direct current from a welding power supply, is used to form an electric arc between the electrode and the metals to be joined. The workpiece and the electrode melts forming a pool of molten metal (weld pool) that cools to form a joint. As the weld is laid, the flux coating of the electrode disintegrates, giving off vapors that serve as a shielding gas and providing a layer of slag, both of which protect the weld area from atmospheric contamination. This is the oldest form of welding and is still popular; however there is not a stick welder in the maker hub.
Training
Overview
The operation of the AR Welding station is simple. First you will select a torch for the type of weld you want to practice and plug in the machine. After that it is a simple matter of setting up an exercise based on difficulty, welding method, and weld type. It is recommended that you start with the pre-programmed exercise to begin and then move on to custom exercises as you become more experienced. The general weld type is determined by what piece is being welded; the options include liner and cylindrical butt, lap, and T joints. Before the exercise begins you will have to calibrate the AR helmet. The calibration process occurs at the beginning of the exercise and is completed by following the instructions given by the AR helmet. After the calibration is completed complete the exercise, view the results, and then repeat.
Demonstration
With the virtual reality welder, students will get the idea as to how the welding machines work, whether that be arc, MIG, or TIG welding. Once students earn a score of 90 or higher on the simulation, they have the opportunity to work with the actual welders in the welding shop.
General Procedure
Setting up Simulator
- Plug in extension cord (make sure it won’t trip anyone) for power.
- Flip switch on back of machine to turn on.
- Press power button on the front of the machine and wait for the system to start up.
- Attach welding process of your choice (see welding processes section down below).
- At login screen, select user. Guest works well.
- Select right or left handed. This is important because it affects the angle the torch should be held at when performing an exercise.
- Open an exercise. There are four choices for creating an exercise: Open, GMAW (MIG), GTAW (TIG), SMAW (Stick). If you know what type of weld you want to practice go for the open exercise because it will allow for the most customization. If this is a new experience, select the type of weld you are practicing and roll with one of the preset courses.
- On the top of the screen the welding parameters are displayed and will be in red if they are not set properly. Use the control panel (pictured below) to adjust them as needed.
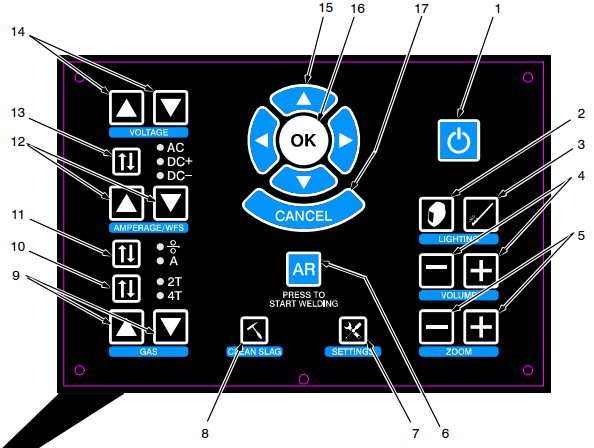 (1) Power On/Off Button Use button to turn system on and off. (2) Helmet Light Control Use button to turn helmet light on and off, and change intensity of light. (3) Filler Rod Light Control (TIG) Control not used with latest software. (4) Volume Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease volume of helmet speakers. (5) Display (Zoom) Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to magnify images on display screens. (6) Augmented Reality (AR) Button Use button to turn augmented reality feature on and off. (7) System Settings Button Use button to access system settings menu. Use the settings menu to change language, units of measure (standard or metric), camera settings and other parameters. After starting an exercise, use the System Settings button to adjust video device settings and optimize AR tracking for the room lighting conditions. (8) Clean Slag Button Use button to remove slag from augmented reality workpiece when Stick and FCAW welding. Slag must be cleaned for test results to be displayed. (9) Shielding Gas Flow Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease the shielding gas flow for the MIG and TIG weld processes. (10) Gun Trigger Selection Button Use button to select either two-step or four-step trigger operation. (11) Amperage/Wire Feed Speed Selection Button Use button to select the weld parameter (amperage or wire feed speed) to be adjusted (see Item 12). (12) Amperage/Wire Feed Speed Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease amperage or wire feed speed (see item 11). (13) AC/Polarity Selection Button Use button to select AC weld output or DCEP or DCEN weld polarity. (14) Voltage Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease weld voltage. (15) System Navigation Buttons Use buttons to navigate AR system programs and select menu items. (16) OK (System Selection) Button Use button to activate selected menu items. (17) System Cancel Button Use button to stop the AR program or activity in use, or return to the previous screen.
(1) Power On/Off Button Use button to turn system on and off. (2) Helmet Light Control Use button to turn helmet light on and off, and change intensity of light. (3) Filler Rod Light Control (TIG) Control not used with latest software. (4) Volume Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease volume of helmet speakers. (5) Display (Zoom) Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to magnify images on display screens. (6) Augmented Reality (AR) Button Use button to turn augmented reality feature on and off. (7) System Settings Button Use button to access system settings menu. Use the settings menu to change language, units of measure (standard or metric), camera settings and other parameters. After starting an exercise, use the System Settings button to adjust video device settings and optimize AR tracking for the room lighting conditions. (8) Clean Slag Button Use button to remove slag from augmented reality workpiece when Stick and FCAW welding. Slag must be cleaned for test results to be displayed. (9) Shielding Gas Flow Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease the shielding gas flow for the MIG and TIG weld processes. (10) Gun Trigger Selection Button Use button to select either two-step or four-step trigger operation. (11) Amperage/Wire Feed Speed Selection Button Use button to select the weld parameter (amperage or wire feed speed) to be adjusted (see Item 12). (12) Amperage/Wire Feed Speed Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease amperage or wire feed speed (see item 11). (13) AC/Polarity Selection Button Use button to select AC weld output or DCEP or DCEN weld polarity. (14) Voltage Adjustment Buttons Use buttons to increase or decrease weld voltage. (15) System Navigation Buttons Use buttons to navigate AR system programs and select menu items. (16) OK (System Selection) Button Use button to activate selected menu items. (17) System Cancel Button Use button to stop the AR program or activity in use, or return to the previous screen. - Place Helmet on head and size to head.
- Follow instructions in the helmet to calibrate the simulator to begin welding.
- Press cancel to exit. There is also an option to view results that is very helpful.
Switching Welding Processes
MIG:
- Take connector of MIG torch and align 4 holes with machine (left side).
- Twist the threaded end, but do not over tighten.
- To remove, unscrew the connector.
Stick
- Grab clamp with small cord attached.
- Align pins with the 5 holes of the connector with the receptacle on the machine (right side).
- To remove, press silver button and softly pull straight out (do not twist).
TIG
- Grab cable with TIG torch attached.
- Align 4 holes of the connector with the receptacle on the machine (left side - same as MIG).
- Screw in while holding the connector (do not over tighten).
- To remove, unscrew the connector.
Clean up
- Take helmet off and place on 2nd shelf of cart.
- Disconnect welding process.
- Exit out of the exercise.
- Press power button on front of the machine and wait for screen to be completely blank.
- Flip the switch to off on the back of machine.
- Unplug the extension cord and leave it coiled up neatly underneath the cart.
- Stack work pieces neatly.
- Coil up all cables of torches used and neatly place on the bottom shelf of the cart.
Safety
- Don’t drop the helmet, always place on cart when your not wearing it
- When someone enters the tool room, make sure they know about the extension cord
- Do not aggressively over tighten the connectors of the welding torches
- Make sure to press silver button when releasing the connector of the stick torch
- Do not cut power to the machine before it is completely shut down (clean up #4 & #5)
- Always lay torches completely on top of the table
- Make sure overhead clamp is secured tightly before using
- Do not scratch the coupons as the simulator needs the markings to read your weld.
Certification
Foxtale Quiz
Troubleshooting
Maintenance
General maintenance
- Make sure the space is kept neat and tidy.
- Dust off the top of the machine if necessary.
- Before leaving, make sure all cords and torches are in their place.
Specific Maintenance Tasks
| Maintenance Procedure | Frequency | Done By |
|---|---|---|
| Sample | Sample | Sample |

